
Last Updated on by lizzy
What is Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (ED), also known as impotence, refers to the consistent inability to achieve or maintain an erection firm enough for satisfactory sexual performance. It is a common condition that can affect men of all ages but becomes more prevalent with increasing age.

Causes of Erectile Dysfunction
Physical Causes
Cardiovascular Conditions
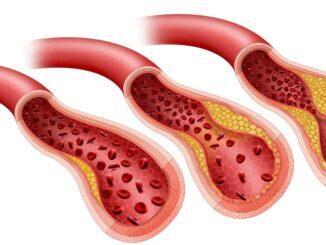
Conditions that affect the heart and blood vessels, such as hypertension (high blood pressure), atherosclerosis (narrowing of the arteries), and coronary artery disease, can impede blood flow to the penis, making it difficult to achieve or maintain an erection.
Diabetes:
Uncontrolled diabetes can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to erectile dysfunction.
Hormonal Imbalances:
Low testosterone levels, also known as hypogonadism, can contribute to erectile dysfunction.
Neurological Disorders
Conditions such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and stroke can disrupt the normal nerve function responsible for initiating and maintaining erections.
Medications and Treatments: Certain medications, such as antidepressants, antihypertensives, and chemotherapy drugs, as well as treatments like radiation therapy, can have side effects that affect erectile function.
Psychological Causes
Anxiety and Stress
Mental health conditions, including anxiety, stress, and depression, can interfere with sexual arousal and performance, leading to erectile dysfunction.
Relationship Issues
Conflicts, poor communication, or unresolved issues within a relationship can contribute to performance anxiety and subsequent erectile problems.
Performance Anxiety
Fear or pressure to perform sexually can create psychological barriers that hinder the ability to achieve or maintain an erection.
Lifestyle Factors
Smoking
Tobacco use damages blood vessels and reduces blood flow, increasing the risk of erectile dysfunction.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Chronic heavy drinking can interfere with sexual function and reduce libido.
Sedentary Lifestyle
Lack of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle can contribute to obesity, cardiovascular problems, and hormonal imbalances that impact erectile function. d. Substance Abuse: Illicit drug use, particularly cocaine and methamphetamines, can negatively affect erectile function.
Other Factors
Age
As men age, they may experience a natural decline in sexual function and a higher likelihood of developing erectile dysfunction.
Obesity
Excess weight and obesity can contribute to hormonal imbalances, cardiovascular issues, and diabetes, all of which can increase the risk of erectile dysfunction.
Chronic Medical Conditions
Chronic kidney disease, liver disease, and certain cancers can affect erectile function due to their impact on overall health and blood flow.
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) and Mental health
The relationship between erectile dysfunction (ED) and mental health is a complex and interconnected one. Mental health issues can both contribute to and result from erectile dysfunction, creating a cycle of negative effects. Let’s explore the correlation between these two aspects:
Anxiety and Stress
- High levels of anxiety can lead to increased muscle tension and a release of stress hormones, which can interfere with the physiological processes necessary for achieving and maintaining an erection.
- The fear of not being able to perform sexually can create pressure and anxiety, exacerbating erectile difficulties.
Depression and Erectile Dysfunction
- Depression and ED may share common biological mechanisms, including neurotransmitter imbalances and vascular problems.
- Loss of Interest and Libido: Depression can cause a decreased interest in sexual activity, leading to reduced sexual arousal and difficulties with obtaining or sustaining an erection.
Symptoms of Erectile Dysfunction
Here are some common symptoms of:
- Difficulty achieving an erection
- Reduced sexual desire:
- Premature ejaculation or delayed ejaculation
- Emotional and psychological distress
- Relationship difficulties
Diagnosis of Erectile Dysfunction
Diagnosing involves a comprehensive evaluation of a person’s.
- Medical History
- Physical Examination:
- Psychological Assessment
- Blood Tests
- Urine Tests
- Nocturnal Penile Tumescence (NPT) test
- Doppler Ultrasound
- Injection Test
Treatment of Erectile Dysfunction
Here are some common approaches :
Lifestyle Changes
- Regular Exercise
- Healthy Diet
- Smoking Cessation:
- Alcohol and Substance Use
Oral Medications
Oral medications, such as phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors, are commonly prescribed as first-line treatment.
Vacuum Erection Devices (VED)
A vacuum erection device is a non-invasive device that creates a vacuum around the penis, drawing blood into the penile tissues to facilitate an erection. A constriction band is then placed at the base of the penis to maintain the erection.
Penile Injections
Medications such as alprostadil can be injected into the base or side of the penis to promote blood flow and induce an erection. This method is generally effective and may be suitable for individuals who do not respond to oral medications.
Intraurethral Suppositories
Alprostadil can also be administered in the form of a suppository that is inserted into the urethra using a special applicator. The medication is then absorbed through the urethral lining to facilitate an erection.
Penile Implants
For individuals who do not respond to other treatments or prefer a more permanent solution, penile implants may be considered. These are surgically implanted devices that allow for on-demand erections. .
Psychotherapy and Counseling
For individuals with psychological factors psychotherapy or counseling can be beneficial. These therapies can help address anxiety, depression, relationship issues, and performance anxiety, which may be hindering sexual function.





Leave a Reply