Last Updated on by lizzy
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a common digestive disorder that occurs when stomach acid flows back up into the esophagus. It affects millions of people worldwide and can cause discomfort and complications if left untreated.

Causes of Acid Reflux
Acid reflux is typically caused by a malfunctioning lower esophageal sphincter (LES), a ring of muscle that normally prevents stomach acid from flowing into the esophagus. However, several factors can contribute to the development . These include:
Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES) dysfunction
When the LES relaxes or weakens abnormally, it allows stomach acid to escape into the esophagus.
Hiatal hernia
A condition in which a portion of the stomach pushes up through the diaphragm, affecting the function of the LES.
Obesity and excess weight
The additional pressure on the abdomen can force stomach acid into the esophagus.
Pregnancy
Hormonal changes and the growing uterus can put pressure on the stomach, leading to the condition.
Certain foods and beverages
Spicy, fatty, or acidic foods, as well as carbonated drinks, caffeine, and alcohol, can trigger or worsen the symptoms.
Symptoms of Acid Reflux
It presents with a range of symptoms, which can vary in severity from person to person. Common symptoms include:
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest that may radiate to the throat.
- Regurgitation: The sensation of stomach acid or food coming back into the mouth.
- Chest pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest, often mistaken for a heart attack.
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia): A feeling of food sticking in the throat or chest.
- Chronic cough: A persistent cough that is not related to a respiratory infection, often worse at night.
Complications of Acid Reflux
If untreated it can lead to complications that affect both the esophagus and other parts of the body. Some potential complications include:
Esophagitis: Inflammation of the esophagus due to constant exposure to stomach acid, causing discomfort and difficulty swallowing.
Barrett’s esophagus: A condition in which the lining of the esophagus undergoes changes, increasing the risk of esophageal cancer.
Esophageal strictures: Narrowing of the esophagus due to scar tissue formation, leading to difficulty swallowing.
Respiratory issues: Chronic aspiration of stomach acid into the lungs can cause respiratory problems, such as asthma, pneumonia, or chronic cough.
Dental problems: The frequent exposure of tooth enamel to stomach acid can result in tooth decay, gum disease, and bad breath.
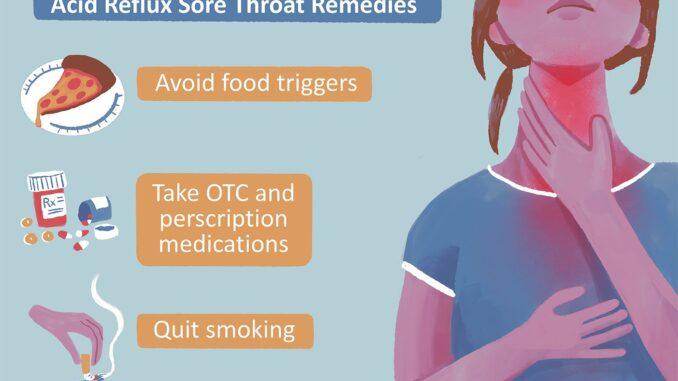
Managing and Treatment of Acid Reflux
The management and treatment aim to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and improve the quality of life. Here are some approaches commonly used:
Lifestyle modifications
This includes weight loss, avoiding trigger foods, elevating the head of the bed, and practicing stress-reduction techniques.
Medications
Over-the-counter antacids, H2 blockers, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can help reduce stomach acid and relieve symptoms.
Surgical interventions
In severe cases or when medications are ineffective, surgical procedures like fundoplication may be considered to strengthen the LES and prevent acid reflux.
Alternative therapies
Some individuals find relief from complementary and alternative therapies such as acupuncture, herbal remedies, and yoga.
Dietary changes and meal planning
Following a balanced diet, including smaller meals, avoiding trigger foods, and adopting healthy eating habits can help manage symptoms.
Acid Reflux common asked questions
What causes acid reflux?
Can be caused by various factors, including a weak lower esophageal sphincter (LES), hiatal hernia, obesity, pregnancy, and certain foods and beverages.
How is acid reflux diagnosed?
It is usually diagnosed based on the patient’s symptoms and medical history. In some cases, diagnostic tests such as endoscopy, pH monitoring, and esophageal manometry may be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
How can I manage and treat acid reflux?
Lifestyle modifications such as weight loss, avoiding trigger foods, elevating the head of the bed, and reducing stress can help in management. Medications like antacids, H2 blockers, and proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) may also be prescribed. In severe cases, surgical interventions may be considered.
When should I seek medical attention for acid reflux?
If you experience frequent or severe acid reflux symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention. Additionally, if you have difficulty swallowing, unexplained weight loss, chest pain, or respiratory issues, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and appropriate treatment.




Leave a Reply